Describe in Words the Structure of a Typical Virus
The capsid and entire virus structure can be mechanically physically probed through atomic force microscopy. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external.
12 1 Viruses Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
Most viruses are in the range of 20200 nm although some viruses can exceed 1000 nm in length.
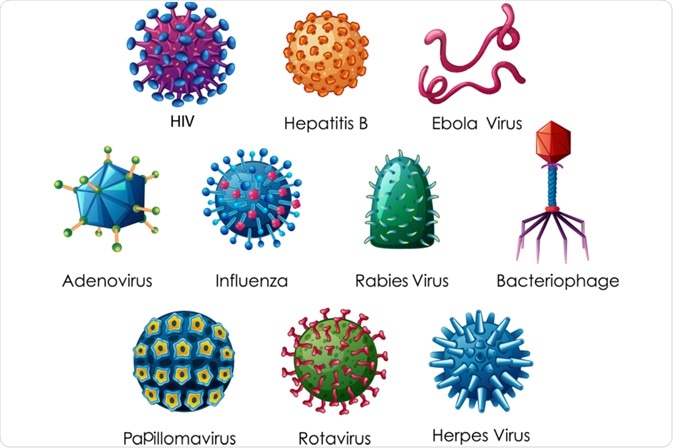
. The nucleic acid encodes the. RNA viruses have an enzyme called reverse transcriptase that permits the usual sequence of DNA-to-RNA to be. Classification based on the mode of transmission.
A virus particle is made up of genetic material housed inside a protein shell or capsid. Theyre named for the distinctive crown-like spikes on the virus surface. Though the details of virus infection and replication vary greatly with host type all viruses share 6 basic steps in their replication cycles.
Penetration or Viral Entry the virus or viral nucleic acid gains entrance into the cell. The life cycle of a virus. Viruses are usually much smaller than bacteria with the vast majority being submicroscopic generally ranging in size from 5 to 300 nanometers nm.
Coronaviruses are a group of viruses that cause a variety of diseases in humans and animals. A typical bacterium is 23. The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell.
Summary of Key Concepts. Virus circulates in human bird and animal causing seasonal epidemic and occasional pandemic outbreaks. A typical virus consists of a protective protein coat known as a capsid.
Some scientists speculate that viruses started as rogue segments of genetic code that adapted to a parasitic existence. Swine flu and Rhinovirus. Some viruses also have an outer.
Describe the structure of a typical virus. Describes the structure of helical icosahedral complex and enveloped viruses. Is the same as other pathogens.
The genetic material or genome of a virus may consist of single-stranded or double. 4 nucleic acid core protein coat or capsid envelope viralviral--specific enzymesspecific enzymes. In the past century the world has faced five.
Herpes simplex virus and the hepatitis B virus are DNA viruses. They can often survive outside a host for long periods of time. In general there are five main morphological virus types.
However bacteriophages viruses that infect bacteria have a unique shape with a geometric head and filamentous tail. The genome is typically surrounded by a protein shell called a capsid composed of protein subunits called. The structure of a virus and how it infects a cell.
What a virus is. Viruses possess either DNA or RNA as their genome. It contains a mosaic of antigens from the host and the virus.
The typical structure of a virion which is the term used to describe a single virus includes an outer shell that is otherwise referred to as the protein capsid or membrane. STRUCTURE OF A VIRUS Viruses contain nucleic acideither DNA deoxyribonucleic acid or RNA ribonucleic acid and protein. All viruses contain nucleic acid either DNA or RNA but.
Viruses are much smaller than bacteria and consist of a single- or double-stranded nucleic acid DNA or RNA surrounded by a protein shell called a capsid. Viruses are small. Viruses generally come in two forms.
Attachment the virion attaches to the correct host cell. Airborne infections Transmission of the virus through the air into the respiratory tract. Envelope-this is an amorphous structure composed of lipid protein and carbohydrate which lies to the outside of the capsid.
Synthesis the viral. The capsid shape varies from simple helical and icosahedra forms to more complex structures with tails. When they do infect a suitable host cell or cells they replicate.
Be sure to discuss the following. Fecal oral route.
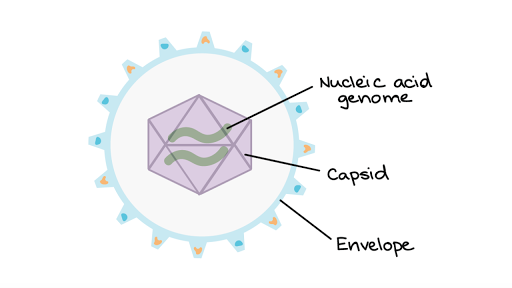
Intro To Viruses Article Viruses Khan Academy

Virus Definition Structure Classification Examples Biology Dictionary

Comments
Post a Comment